What is SHINRA?
Required software
- HyperWorks (Altair Engineering)
- NX (Siemens)
Functions List
- Feature label recognition function
- Feature label is done for each surface
- Customization for the recognized feature label
- Model similarity finder function
- Searching for the closest similar model
Features
- A 3D model can be transformed into a group of surfaces, where each surface is treated as a unit of data
In general resin part will have about few thousand surfaces in one model that can be used for training data
⇒Only several CAD models are necessary to create a pre-trained AI system, which is inevitable in practical use where no big-data is available - High-speed computation by dimension reduction (3D geometrical data into 1D data)
- AI that uses 3D geometrical data as input will need a lot of time to compute
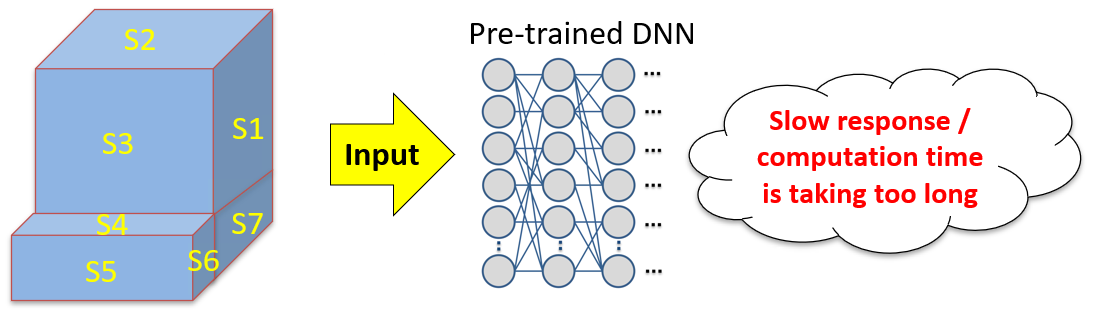
- Tremendous amount of time saving can be expected by dimension reduction from 3D into 1D
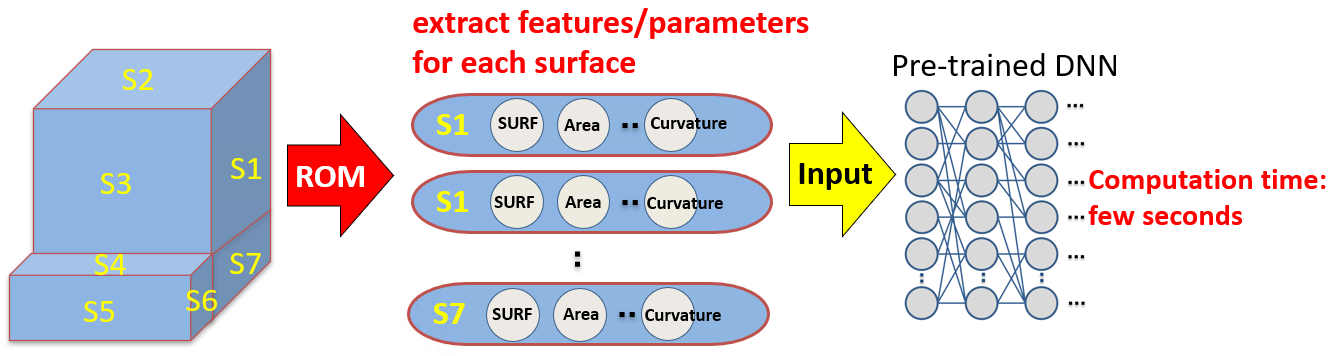
- AI that uses 3D geometrical data as input will need a lot of time to compute
- Patent Trademark "Surface Shape Determination Device, Method and Program" (Japan Patent No. 6605712, 6806321, 7189584)
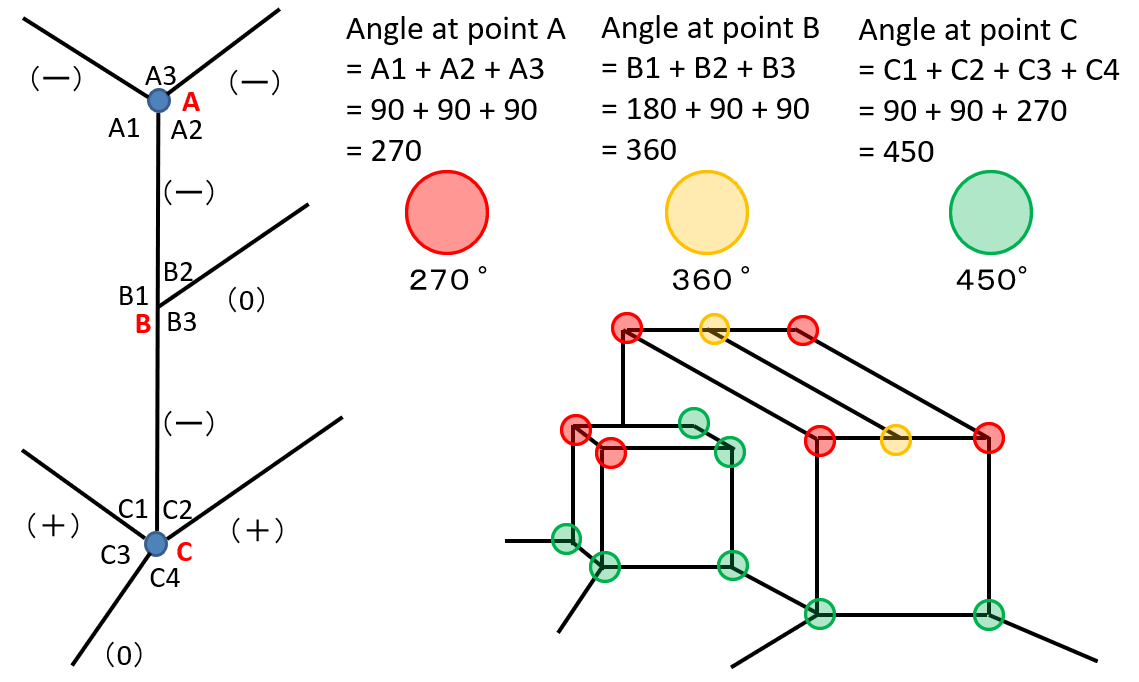
- SURF Methodology
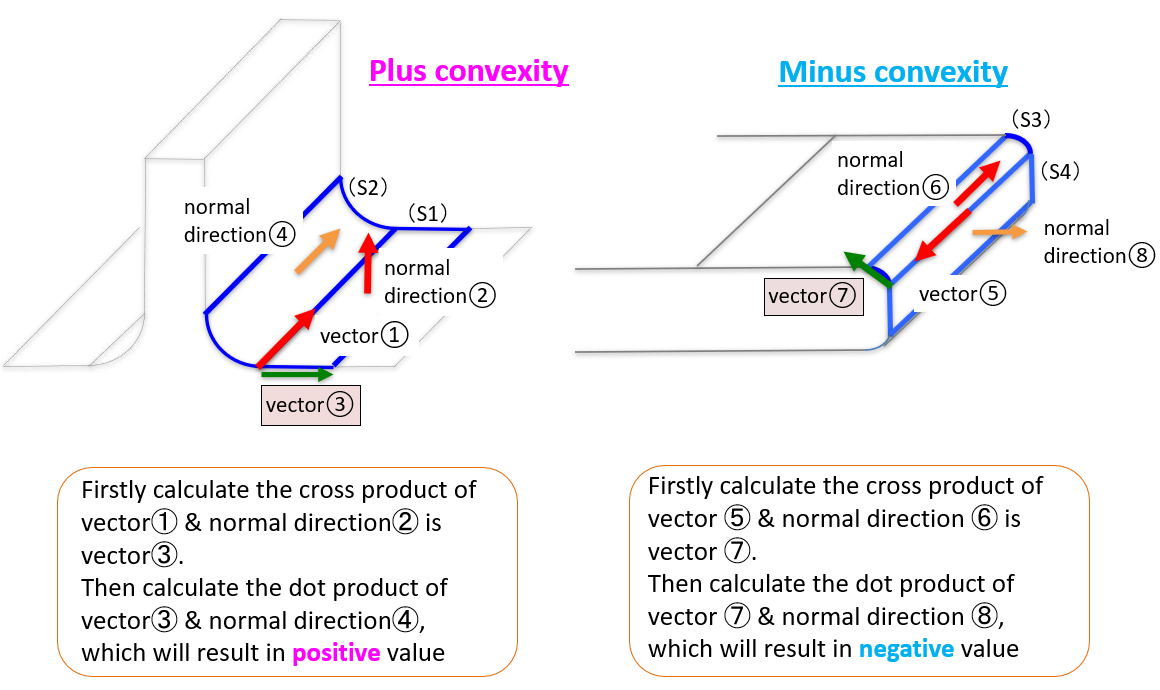
- Point Angle Principle
Feature label recognition function
Overview
- Using AI to automatically recognize feature labels for 3D objects
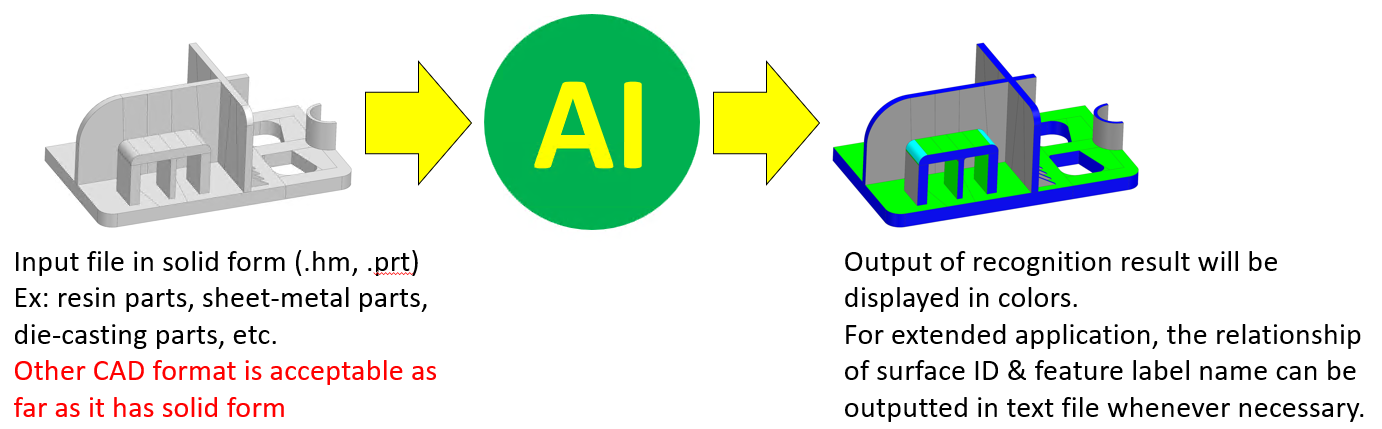
- The definition of feature labels can be freely determined by users
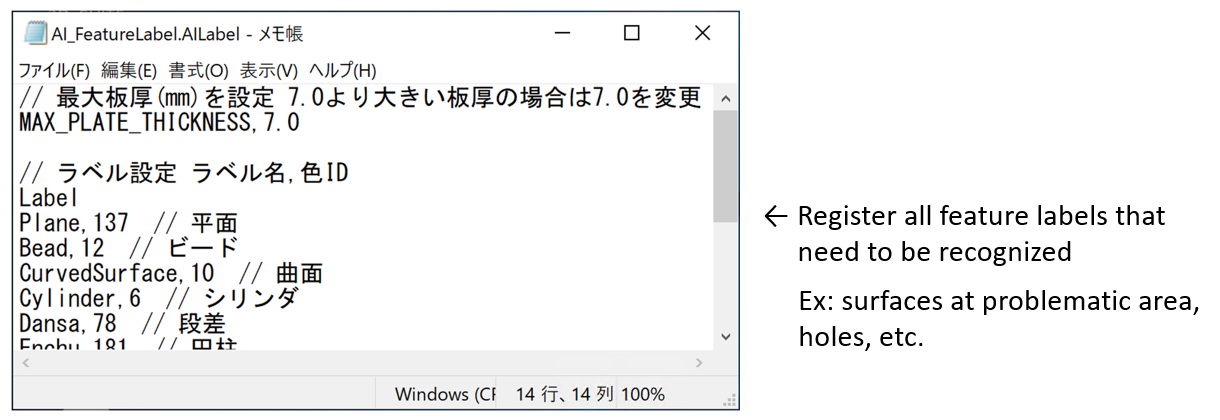
- Customization can be made optionally for feature label results from AI
(Example:)Surface division, elimination of fillets, etc.
Study Case
- Aluminum casting products
- Feature label for each surface
- combustion chamber, water jacket, oil pan, etc.
- AI prediction with accuracy of 90% was achieved by just using 9 models as training data
- CAD/CAM
- Necessary process to prevent mesh generation failure, line splitting for area that has thermal boundary conditions, etc.
- About 50% reduction of workload burden on human operators
- Setting of thermal boundary conditions
- Mesh size refinement at some areas
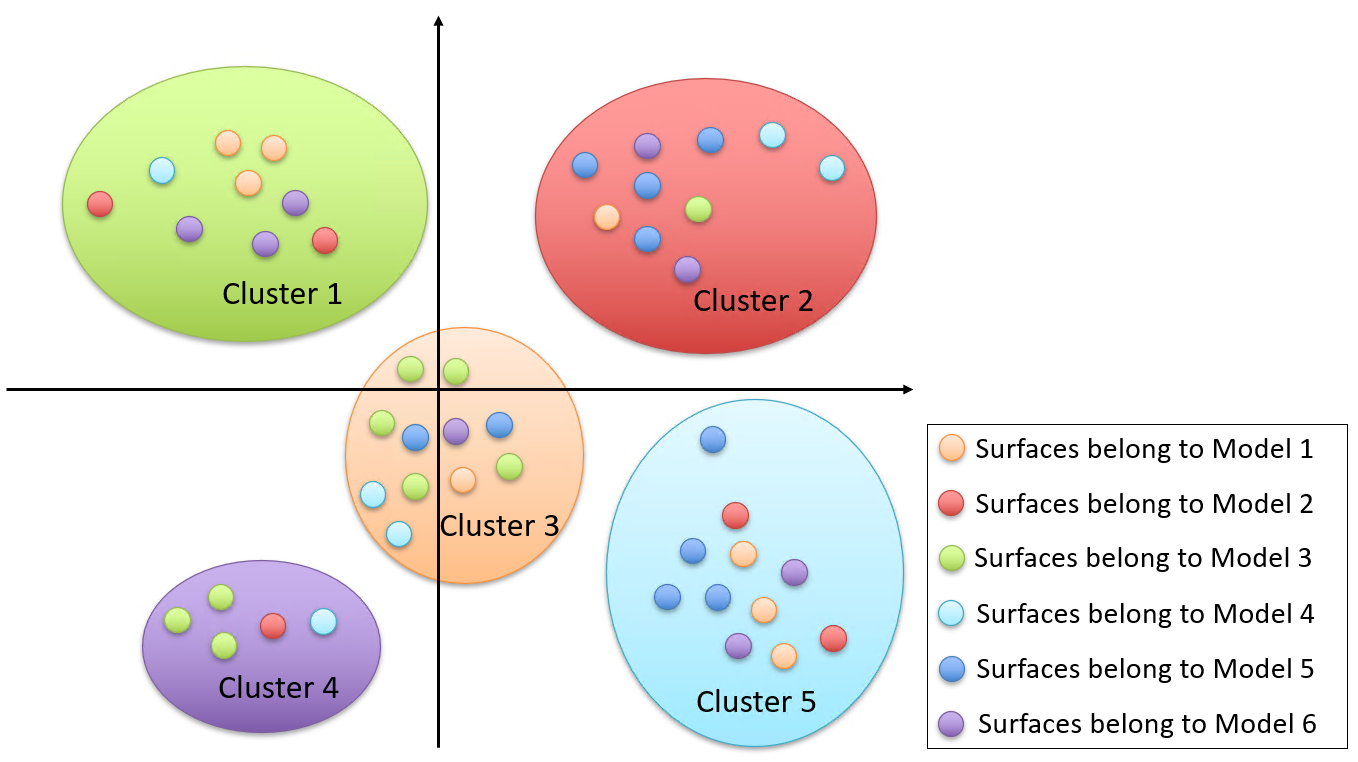
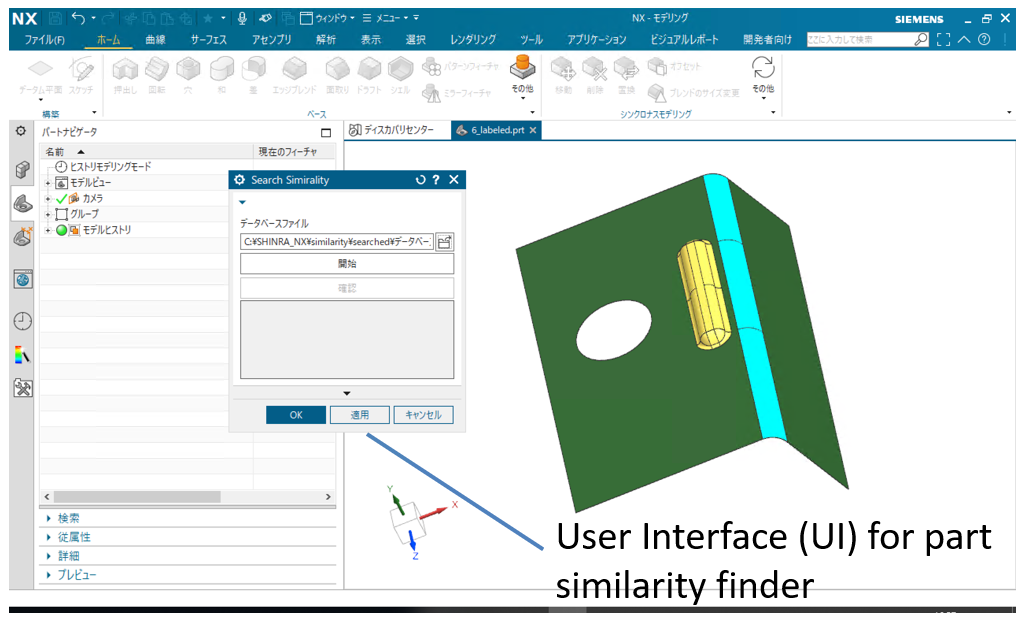
Model similarity finder function
Overview
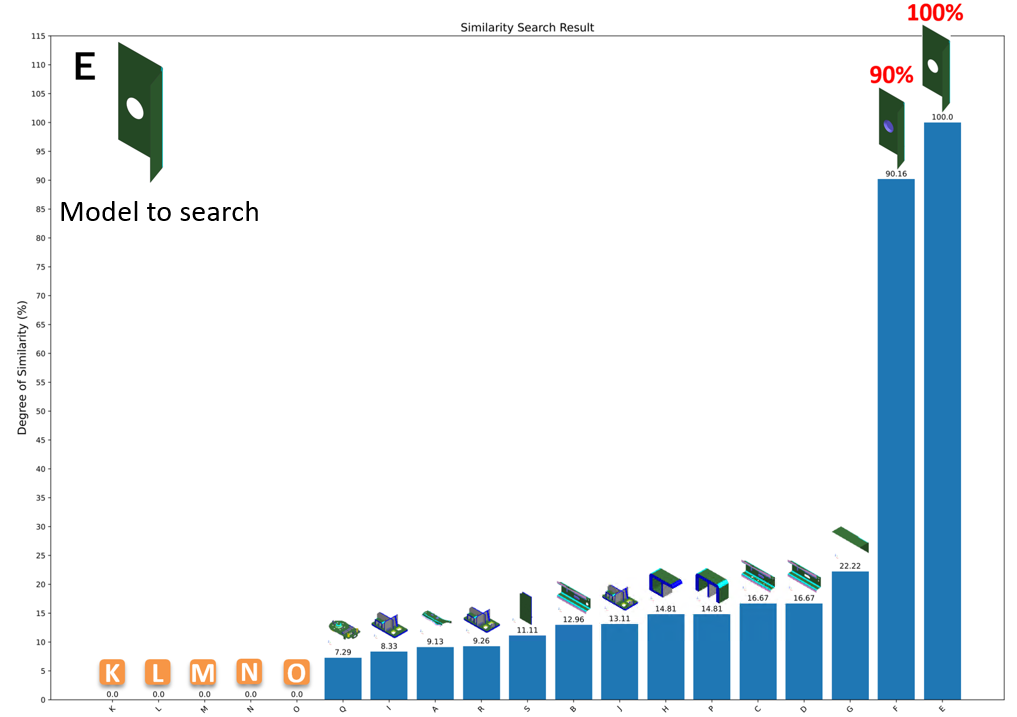
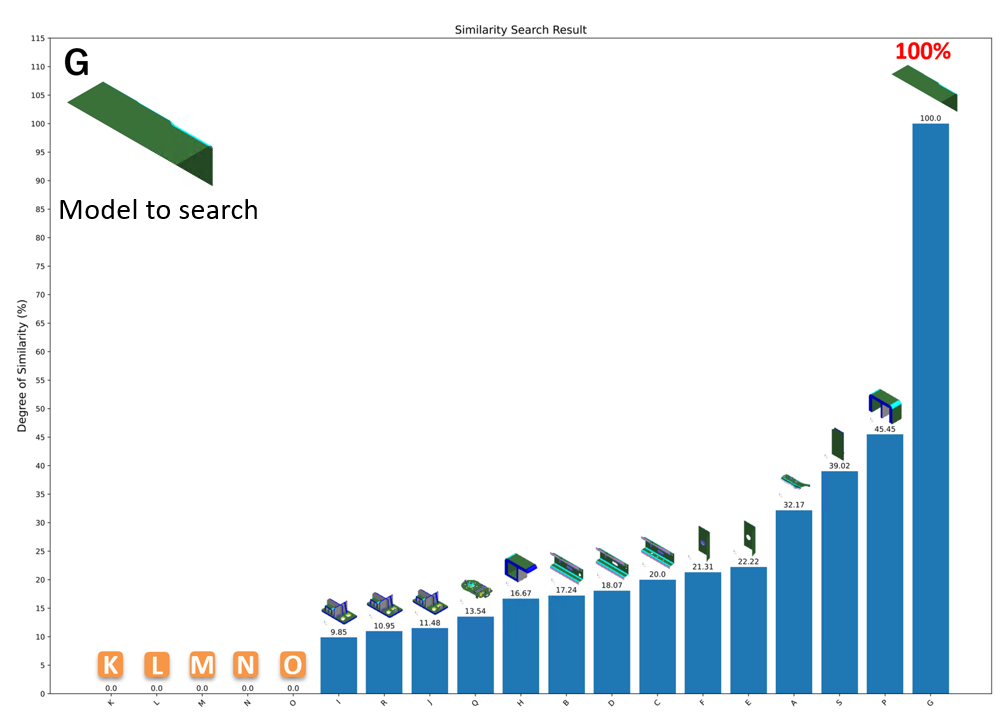
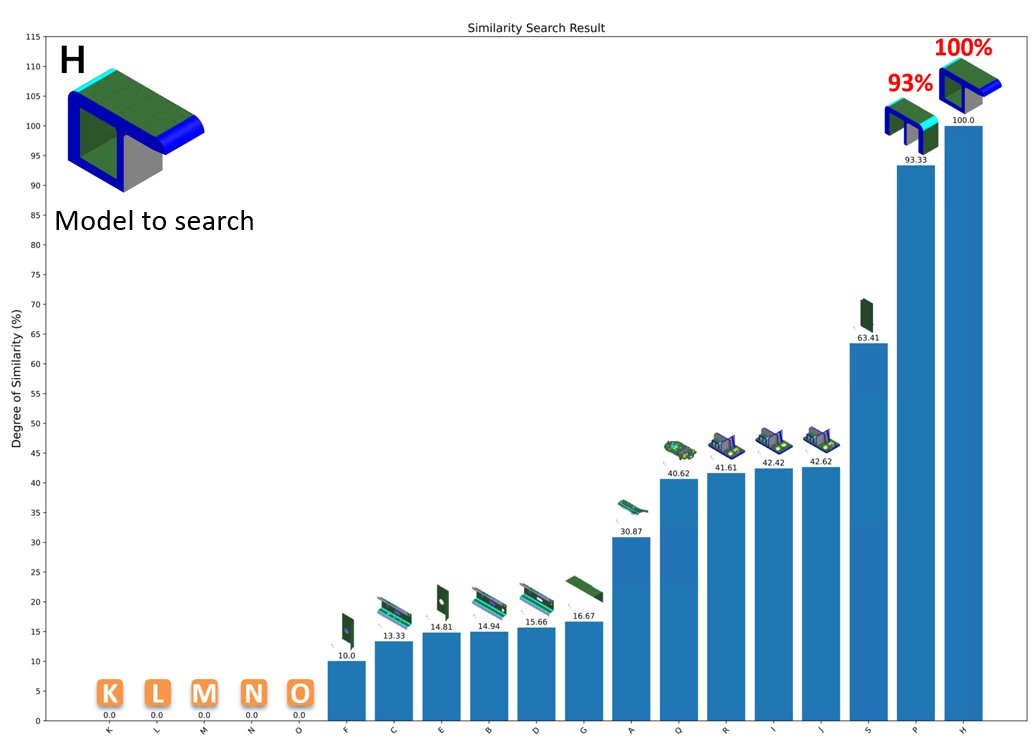
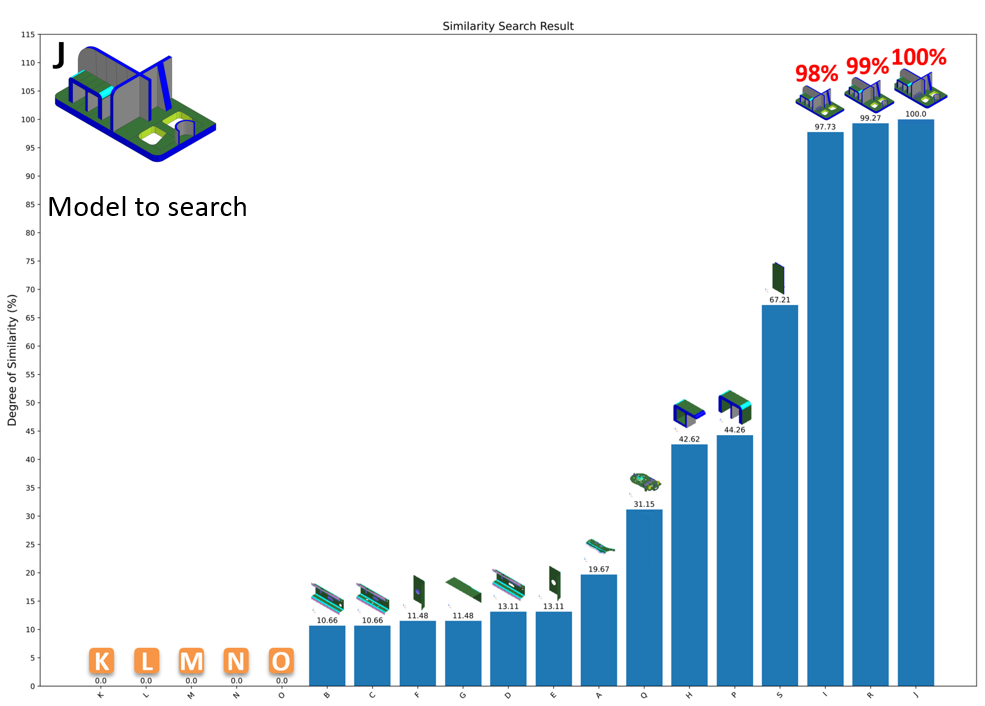
Find the most similar model from all the models registered in the database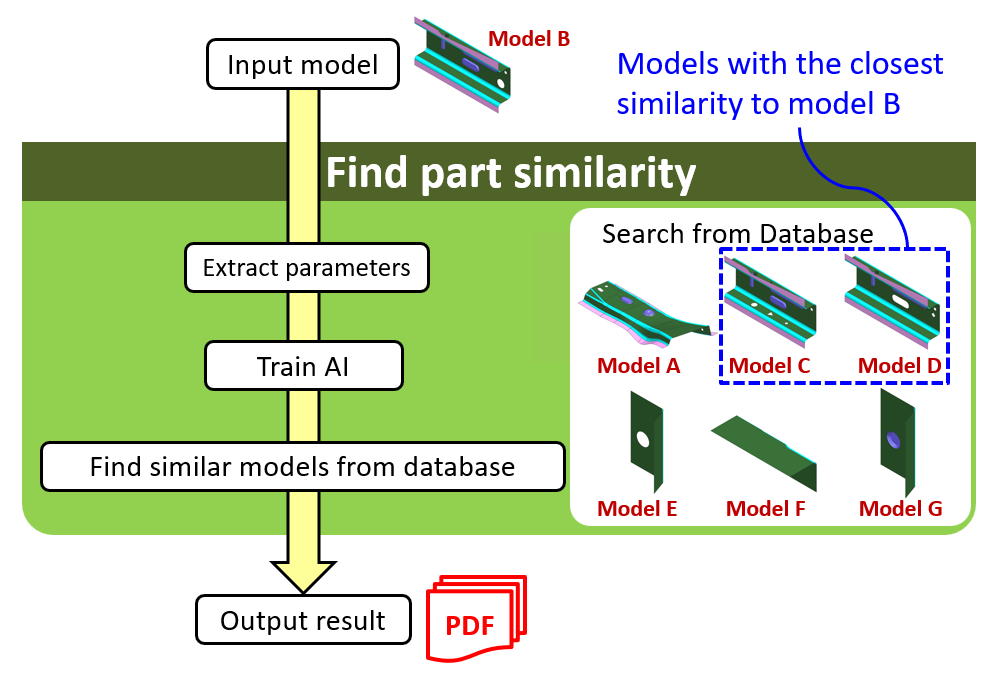
Searching result will be output in PDF file shown by two types of graphs
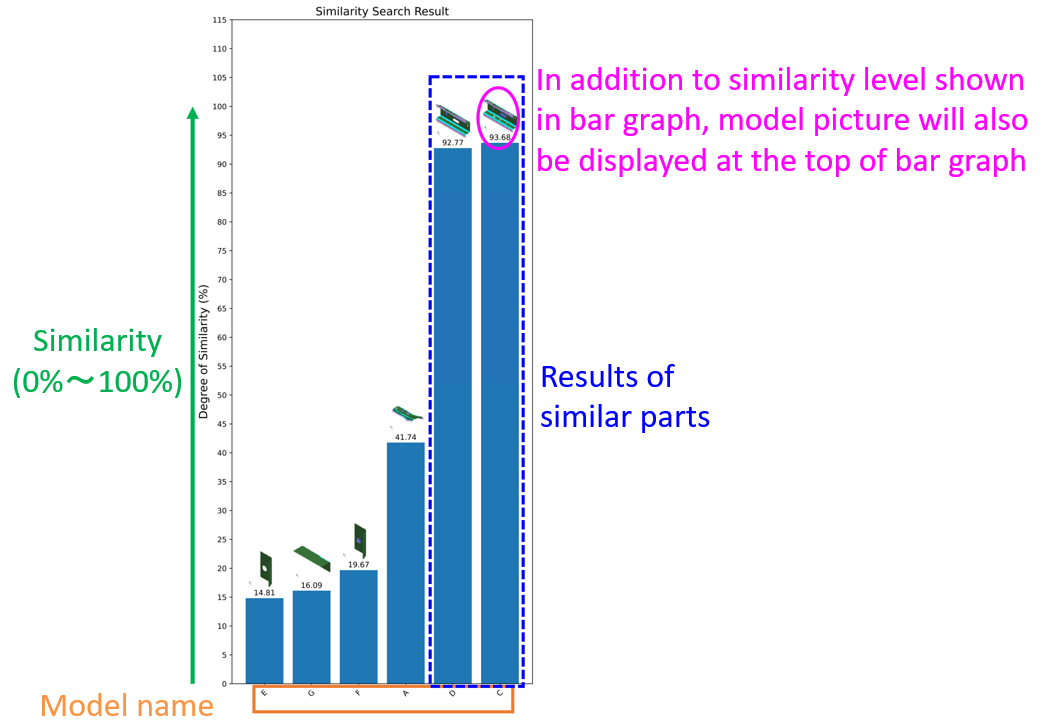
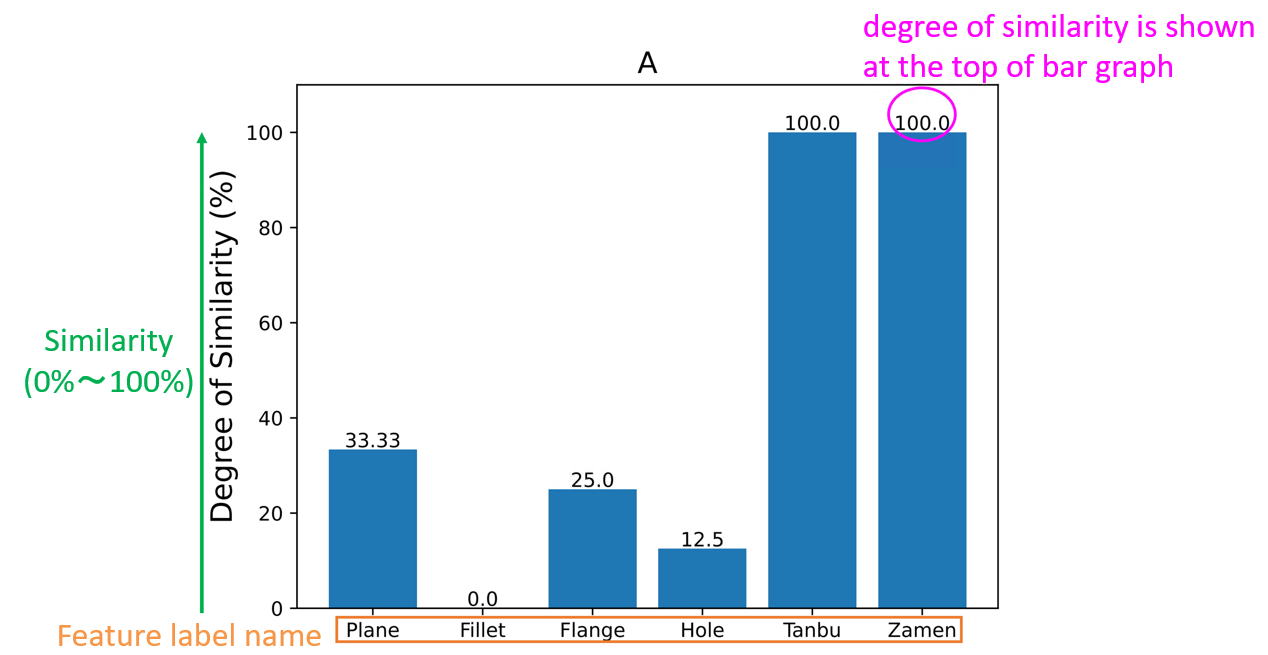
An example of other model similarity finder
Application
Database registration/management by part number
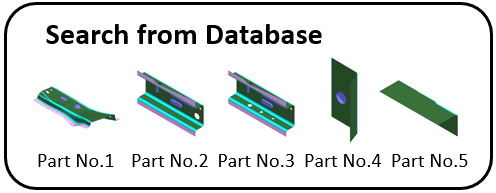
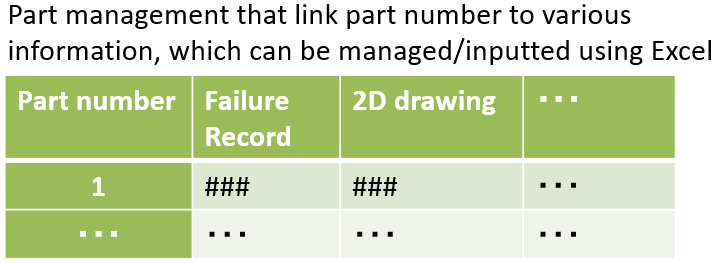
Retrieval of part number for the most similar model

Retrieval of all properties attached to part number
- Confirm the history for malfunction/defect report
Part No.4 has defect report at fillet
⇒ Fillet feature similarity is 100%, so this new model may have a high probability of malfunction/improper design.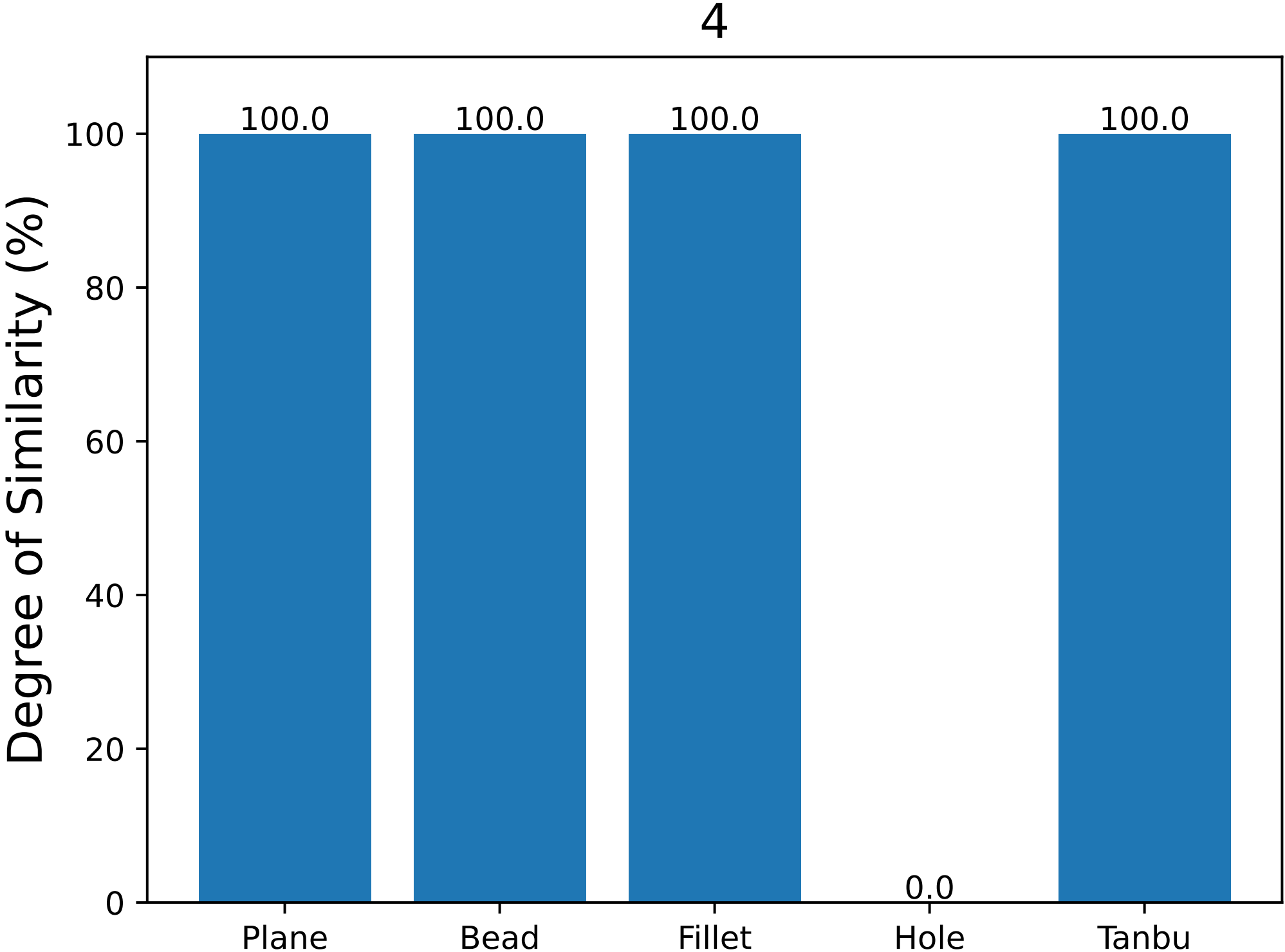
- Confirmation of 2D drawing
Retrieval of 2D sketch drawing of the most similar model
⇒ Make new design based on the previous data of 2D drawing from the most similar model
AI can be used to replace the necessity of technical meeting/discussion for new design
How to use
Model similarity finder has two ways of operation.Lets assume two different conditions in 3.1, 3.2
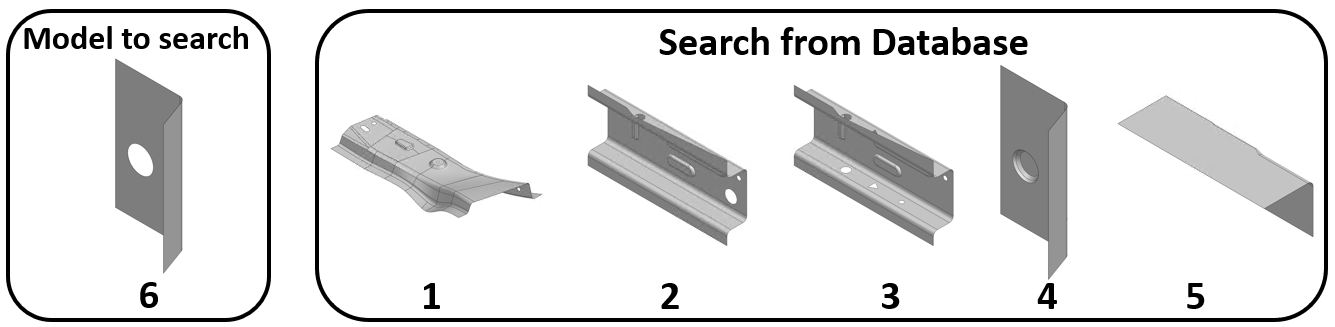
Feature labels are provided by users
- Using SHINRA to recognize all feature labels at each surface for all the models to register as database & the target model to search.
※ Feature labels result from AI prediction is not perfectly accurate, so manual work might be necessary when the predicted labels went wrong.
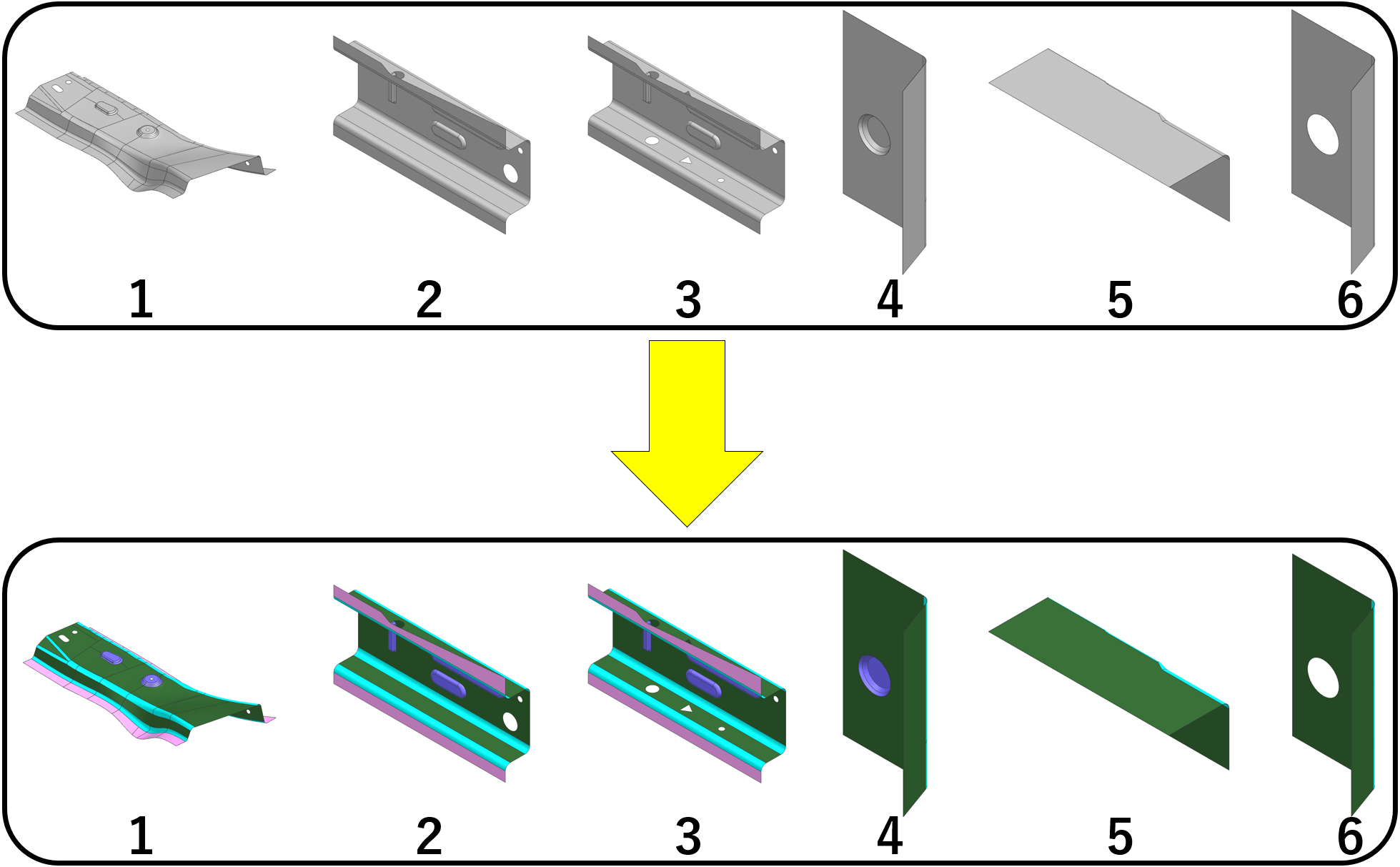
- It is advisable to store the database in your local computer.
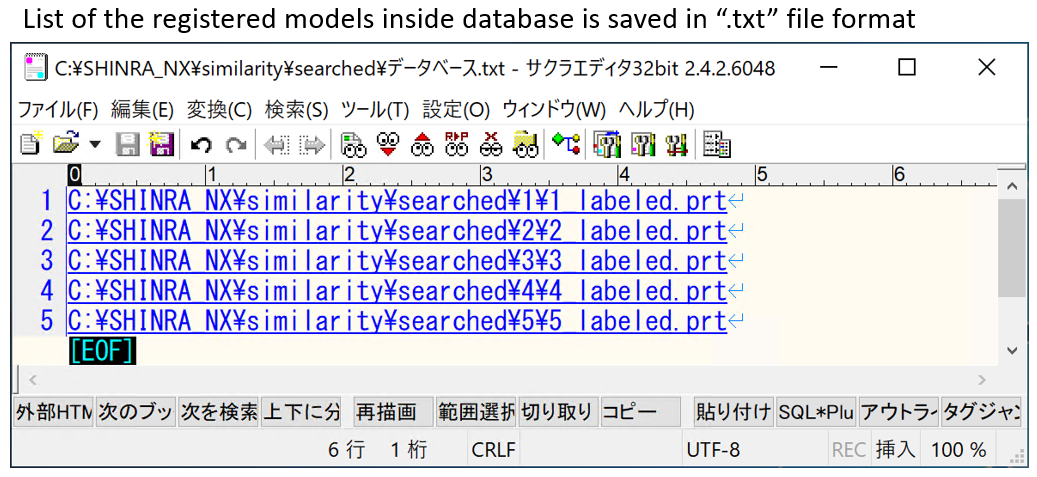

- Open the target model to search, and start finding the most similar model using User Interface (UI).
Feature labels are automatically recognized(Japan Patent Application No.PCT/JP2023/046472)
- Applying AI clustering to automatically recognize feature labels for all the models to register as database & the target model to search.